Describe the Fate Metabolism and Functions of Carbohydrates
Discuss the structures and functions of carbohydrates. Inhibits the breakdown of proteins for energy as they are the primary source of energy.
Carbohydrate Metabolism Anatomy And Physiology Ii
Carbohydrates are used in human metabolism as the primary source of energy in your body but restricting your intake of carbohydrates may help with short-term weight loss.
. HMP Pathway or Pentose Phosphate Pathway and 5. This process takes place primarily in the liver during periods of low. An enzyme by name amylase assists in the breakdown of starch into glucose finally to produce energy for metabolism.
The anabolic processes of carbohydrates include. The goal of digestion and absorption of carbohydrates is to break them down into small molecules of sugar known as glucose. Differentiate alpha and beta carbohydrates.
Describe the fate metabolism and functions of carbohydrates. List the major steps in carbohydrate metabolism and note which require oxygen Describe the major steps and organs involved in lipid and protein metabolism Compare the absorptive and post-absorptive states in terms of glucose use and nutrient transport. Most importantly they provide the energy for the most obvious functions of our body such as moving or thinking but also for the background functions that most of the time we do not even notice 1.
Building bodys components - such as creating the phospholipids of the plasma membrane or building muscle tissue. Carbohydrates are an essential part of our diet. 1 Overview Of Nutrition And Health 2 Digestion And Absorption 3 Carbohydrates 4 Lipids 5 Protein 6 Metabolism Energy Balance And Body Composition 7 Weight Management 8 The Vitamins 9 Water And The Minerals 10 Fitness And.
Although they are found in different forms carbs are broken down into simple units through digestion to be used in metabolism. Carbohydrates act just like the fuel in our cars. There are different ways in which carbohydrates helps living beings like storing energy in the form of glycogen and starch.
Sec 253 Carbohydrate Metabolism 16 How many reactions take place during. It helps in transporting energy to. Easy Study Objective 1.
The primary role of carbohydrates is to supply energy to all cells in the body. SO 253 Describe the fate metabolism and functions of carbohydrates. EbkNutrition Diet Therapy.
Digestive fate of dietary carbohydrates. Plants build carbohydrates using light energy from the sun during the process of photosynthesis while animals eat plants or other animals to obtain carbohydrates. Metabolism of Carbohydrates.
Carbohydrates are one of the major forms of energy for animals and plants. They are energy production energy storage building macromolecules sparing protein and assisting in lipid metabolism. As with other food components the digestive fate of particular carbohydrates depends on their inherent chemical nature and on the supramolecular structures within foods of which they are a part.
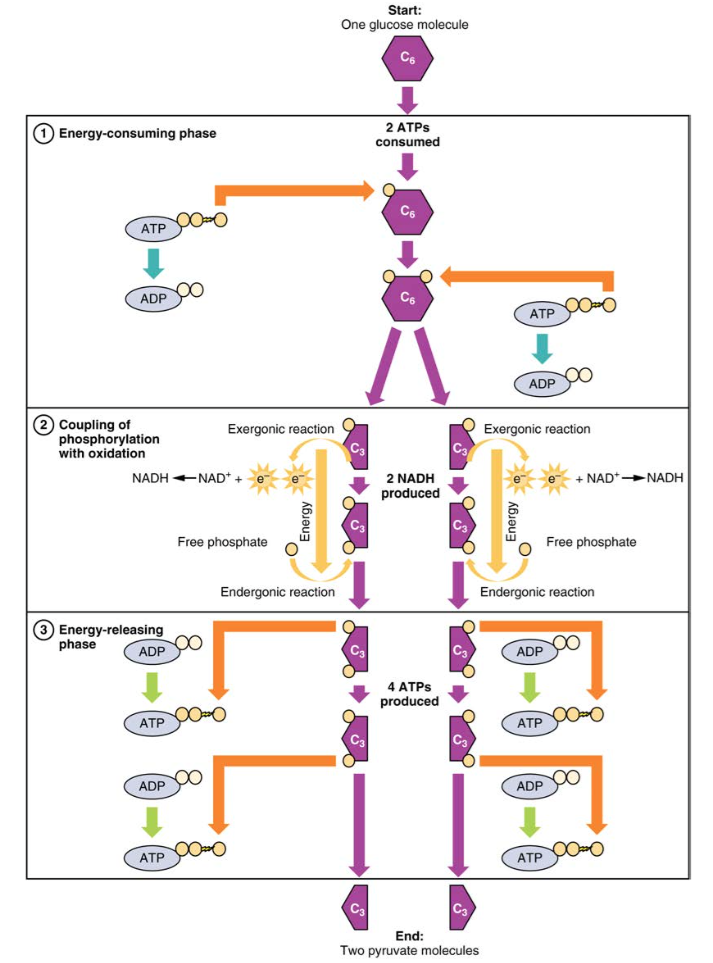
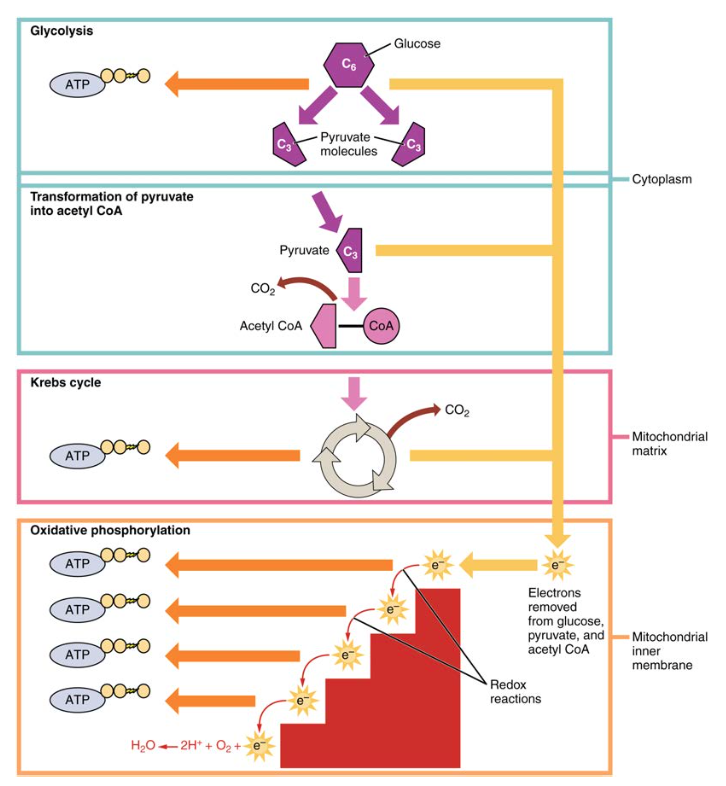
This review will focus on the. The most important carbohydrate is glucose which can be broken down via glycolysis enter into the Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation to generate ATP. List several common sources of carbohydrates.
Citric Acid Cycle 3. The three types of carbohydrates are. K Mg 2 and Ca 2 for example in cardiac contraction and the biosynthesis of complex macromolecules such as glycogen.
15 The net result of the complete oxidation of glucose does NOT include. The energy released is used to power the cells and systems that make up your body. 6 Essential Carbohydrates Functions.
Exergonic give off energy stored in molecules. Glucose is a primary fuel that. By Renee Thompson Updated December 20 2018.
During digestion carbohydrates that consist of more than one sugar get. SO 253 Describe the fate metabolism and functions of carbohydrates. Carbohydrates are also known as starch simple sugars complex carbohydrates and so on.
When we take in carbohydrates we are taking in fuel for our bodies to use for metabolism of our cells. We take in carbohydrates in the form of vegetables fruits. Although the carbohydrates functions are similar to the fuel in our cars the process is much more complex than that.
Energy is required for mechanical work contraction and cellular movement active transport of ionssubstrates ie. The synthesis of glycogen from glucose which requires UTP and therefore ATP. A water b carbon dioxide c ATP d oxygene waste heat Answer.
Figure 2426 Carbohydrate Metabolism. To maintain cellular and whole-body function living organisms require energy continuously. The glucose thermostat is located within the cells of the pancreas.
The metabolism of carbohydrates is done through two processes. The catabolic processes of carbohydrates include. In most animals and in man when dietary carbohydrates are in excess the oxidation of a part of glucose maintains relatively high concentrations of ATP NADH and NADPH.
Metabolic enzymes catalyze catabolic reactions that break down carbohydrates contained in food. A Aid in glycogenesis b Inhibit gluconeogensis c Inhibit lipogenesis d Promote glycolysis e Promote gluconeogenesis Answer. It is also involved in fat metabolism and prevents ketosis.
Since carbohydrate utilization promotes human survival genes and traits regulating carbohydrate metabolism during exercise and energy storage have been selected throughout evolution. Break down of molecules - for example producing energy from glucose. Digestion Metabolism of Carbohydrates.
After eating a meal containing carbohydrates glucose levels rise in the blood. Gluconeogenesis is the synthesis of new glucose molecules from pyruvate lactate glycerol or the amino acids alanine or glutamine. It helps in cell signalling as glycolipids and glycoproteins that act as determinants of blood groups.
2 However current lifestyles are pre-dominantly sedentary which coupled with the intake of excessive amounts of carbohydrates has led to metabolic diseases such as type 2 diabetes. The Functions of Carbohydrates in the Body There are five primary functions of carbohydrates in the human body. Catabolic Processes and B.
Excess or unutilized energy is stored as fat or glycogen for later use. Functions of carbohydrates in our body. Sec 253 Carbohydrate Metabolism 22 Thyroid hormones.
Carbohydrate metabolism is a fundamental biochemical process that ensures a constant supply of energy to living cells. Medium Study Objective 1. Carbohydrate metabolism involves glycolysis the Krebs cycle and the electron transport chain.
Insulin-secreting cells in the pancreas sense the increase in blood glucose and release the hormone insulin into the blood. Plants store carbohydrates in long polysaccharides chains called starch. Transformation of Carbohydrates into Lipids.

Influence Of Insulin And Ppara On Carbohydrate Metabolic Pathways Download Scientific Diagram
No comments for "Describe the Fate Metabolism and Functions of Carbohydrates"
Post a Comment